Google has been fined €2.4bn ($2.7bn; £2.1bn) by the European Commission after it ruled the company had abused its power by promoting its own shopping comparison service at the top of search results.
The amount is the regulator’s largest penalty to date against a company accused of distorting the market.
The ruling also orders Google to end its anti-competitive practices within 90 days or face a further penalty.
The US company may decide to appeal.
If it fails to change the way it operates the service within the three-month deadline, it could be forced to pay 5% of its parent company Alphabet’s average daily worldwide earnings.
Google had previously suggested that Amazon and eBay had more influence over the public’s spending habits and that the commission’s views “failed to fit the reality of how most people shop online”.
However, the decision could set a precedent that determines how the EU’s civil service handles related complaints about the prominence Google gives to its own maps, flight price results and local business listings within its search tools.
Fast growth
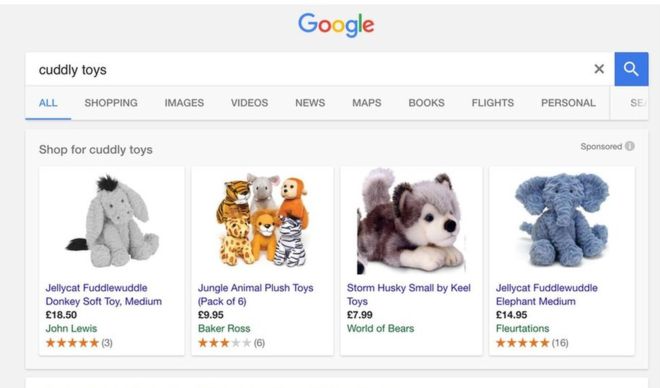
Google Shopping displays relevant products’ images and prices alongside the names of shops they are available from and review scores, if available.
The details are labelled as being “sponsored”, reflecting the fact that, unlike normal search results, they only include items that sellers have paid to appear.
On smartphones, the facility typically dominates “above-the-fold” content, meaning users might not see any traditional links unless they scroll down.
Google also benefits from the fact the Shopping service adverts are more visual than its text-based ads.
One recent study suggested Shopping accounts for 74% of all retail-related ads clicked on within Google Search results. However, the BBC understands Google’s own data indicates the true figure is smaller.
Seven-year probe
The European Commission has been investigating Google Shopping since late 2010.
The probe was spurred on by complaints from Microsoft, among others.
The rival tech giant has opted not to comment on the ruling, after the two struck a deal last year to try to avoid such legal battles in the future.
But one price comparison service has welcomed the fine.
“An entire industry has suffered because of Google’s unlawful, anticompetitive behaviour, and it has become a genuine struggle for survival for the likes of [us],” the chief executive of Kelkoo Richard Stables told the BBC.
“At the same time, Google’s abuse has raised costs for merchants, and it has meant higher prices for consumers and much more limited choice.”
Although the penalty is record-sized, it could have been bigger.
The commission has the power to fine Alphabet up to 10% of its annual revenue, which was more than $90bn (£70.8bn) in its last financial year.
Alphabet can afford the fine – it currently has more than $172bn of assets.
But one expert said the company would be more concerned about the impact on its future operations.
“If it has to change the appearance of it results and rankings, that’s going to have an impact on how it can monetise search,” said Chris Green, from the tech consultancy Lewis.
“Right now, the way that Google prioritises some of its retail and commercial services generates quite a lot of ad income.
“When you consider the sheer number of search queries that Google handles on a daily basis, that’s a lot of ad inventory going in front of a lot of eyeballs.
“Dent that by even a few percentage points, and there’s quite a big financial drop.”
Europe v US tech:
This is far from the first time the European Commission has intervened to penalise US technology companies for what it views to be bad behaviour.
Others to have been targeted include:
- Microsoft (2008) – the Windows-developer was fined €899m for failing to comply with earlier punishments, imposed over its refusal to share key code with its rivals and the bundling of its Explorer browser with its operating system. Five years later, it was told to pay a further €561m for failing to comply with a pledge to provide users a choice screen of browsers
- Intel (2009) – the chip-maker was ordered to pay €1.06bn for skewing the market by offering discounts conditional on computer-makers avoiding products from its rivals. Intel challenged the fine, and a final court ruling in the matter is expected in 2018
- Qualcomm (2015) – the chip-maker was accused of illegally paying a customer to use its technology and selling its chipsets below cost to push a rival out of the market. If confirmed, it faces a fine that could top €2bn, but the case has yet to be resolved
- Apple (2016) – Ireland was ruled to have given up to €13bn of illegal tax benefits to the iPhone-maker since 1991, and was ordered to recover the funds plus interest from the company. However, Dublin missed the deadline it was given to do so and has said it will appeal
- Facebook (2017) – the social network agreed to pay a €110m fine for saying it could not match user accounts on its main service to those of WhatsApp when it took over the instant messaging platform, and then doing just that two years later
The commission is also investigating Amazon over concerns that a tax deal struck with Luxembourg gave it an unfair advantage.
The European Commission continues to pursue two separate cases against Google.
The first involves allegations that the technology company has made it difficult for others to have their apps and search engines preinstalled on Android devices.
The second covers claims Google took steps to restrict rivals’ ads from appearing on third-party websites that had installed a Google-powered search box.
Source: BBC




